Vocational Teacher Job Description
Due to the nature of vocational education, expert-level skill in their subject is essential for vocational teachers. The ability to communicate well with the age group of their students is also very important. Younger students will need more of a supervisory instructor, while older students will often need mentoring or counseling. Depending on the grade level taught, vocational teachers will impart an increasingly detailed level of knowledge. The goal of a career and technical education teacher is to equip students with the skills and tools they will need to enter a particular occupation.
Vocational Teacher Requirements and Common Tasks
Career tech teachers are involved in a wide variety of tasks in their day-to-day work. Instructing students is a vocational teacher’s first priority. A vocational teacher plans lessons and gives them to a group of students, often demonstrating how to safely accomplish a certain task using the proper tools and equipment. Vocational subject instruction frequently involves various types of equipment, and teachers must instruct and supervise students in the use and care of these tools. Like other teachers, vocational teachers assess students on their progress and test them using evaluations. They also may meet with parents of students in middle and high school to discuss their progress or any behavioral issues. Tasks demonstrated and given to students to learn are often hands-on and may include changing the tire on a car or writing code.
Vocational teachers most frequently instruct courses in one of 16 major career fields, which in the field of career and technical education are known as career clusters. These clusters include the areas listed below:
- Agriculture, Food & Natural Resources
- Architecture & Construction
- Arts, A/V Technology & Communications
- Business Management & Administration
- Education & Training
- Finance
- Government & Public Administration
- Health Science
- Hospitality & Tourism
- Human Services
- Information Technology
- Law, Public Safety, Corrections & Security
- Manufacturing
- Marketing
- Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics
- Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
How to Become a Vocational Teacher
Becoming a career and technical education teacher usually involves earning a bachelor’s degree in a teachable career field, followed by earning state certification or licensing for those teaching in public K-12 schools. Many schools offer bachelor’s degrees in career and technical education to help future educators prepare for vocational teaching careers. Prospective educators should choose a program approved by its state board of education for the preparation of teachers, as this is a common requirement for teacher licensure. In addition to education, another common requirement for vocational teachers is to have experience in the field. Since they are teaching students to become proficient in practical career skills, they should ideally have extensive experience in performing those skills themselves. The most common pathway to becoming a vocational teacher in a public K-12 school is as follows:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree in the subject you wish to teach or in career and technical education.
- If your area of expertise requires a state license to practice, as is the case in fields like nursing or accounting, apply for the necessary license or credential.
- Accumulate several (ideally, five) years of experience working in a teachable vocational field, if required.
- Complete a student teaching internship in a career tech classroom if certification is required.
- Take your state’s required exams for teachers.
- Apply for your vocational teaching license.
- Begin applying for open career and technical education jobs.
Many states also offer specialized alternative teacher certification pathways for career and technical education teachers. In some states, this allows educators to enter the career tech field with only an associate’s degree or a high school diploma, along with at least five years of relevant work experience. Most states require a period of student teaching or other supervised teaching experience in order to qualify for a teaching certificate, which is required in public K-12 schools. In some career tech subjects, like accounting, a master’s degree in the subject to be taught may be preferred by some schools. Earning a graduate degree can also help vocational teachers qualify for teaching positions in colleges and/or universities.
Vocational Teacher Salary and Job Outlook
Salaries for vocational teachers are affected by many factors including location, educational attainment, subjects taught, and job experience. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that as of 2022, career and technical education teachers in middle schools had a median annual wage of $62,630, in high schools a median annual wage of $62,500, and in postsecondary settings a median annual wage of $59,840.1-3 Job growth for vocational teachers is expected to be around 2% through 2031, which is slower than average for all occupations.4 This limited growth is due in part to a refocus on more traditional core subjects such as English and math due to federal testing requirements that impact school funding. However, as the need increases for workers with technical skills, there may be higher demand for vocational teachers.4
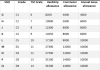
| Career/Technical Education Teacher Level | Number Employed1-3 | Median Annual Wage1-3 | Projected Job Growth 2021-314 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle School | 11,110 | $62,630 | 3% |
| Secondary School | 88,280 | $62,500 | 3% |
| Postsecondary | 103,100 | $59,840 | 2% |
Vocational Teacher Career Interviews
- President, Alabama Association of Agricultural Education, Kelly Pritchett Mullins
Helpful Skills and Experience
Organizational skills, excellent communication and presentation skills, and sound decision-making skills are important for prospective teachers, and vocational teachers are no exception. Career and technical education teachers should be calm, fair, and patient, and be able to work with students of a variety of backgrounds and levels. Technical acumen and advanced education and/or certifications in a specialty subject will make a career tech teacher more desirable. Having at least five years of work experience in a related area is a common requirement for vocational educators.
Possible Job Titles for This Career
- Technical Teacher
- Career and Technical Education (CTE) Teacher
- Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Teacher
- Vocational Teacher
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Do I need teacher certification to teach in a vocational school?
Answer: You may or may not have to obtain teacher certification before beginning to teach at a vocational school. Requirements vary from state to state, between public and private schools, and between secondary and postsecondary schools. Private schools may not require state certification. You can check with your state board of education or college program for further information on certification requirements in your state.
Question: What types of courses do I take to become a vocational teacher?
Answer: Vocational teachers are usually required to take courses in their particular subject area. For example, a vocational teacher in hospitality and tourism may need to have taken courses like accounting. Just as importantly, vocational teachers also typically have hands-on occupational experience in their chosen field. Talk to your school’s advisor or refer to your state board of education to find out what courses are required in your state.
Question: What is a vocational teacher?
Answer: A vocational teacher, also known as a career and technical education teacher, is a teacher of an occupational subject, such as culinary arts, nursing, computer programming, and cosmetology. Unlike teachers of other subjects, vocational teachers typically have extensive experience and/or certification in their field.